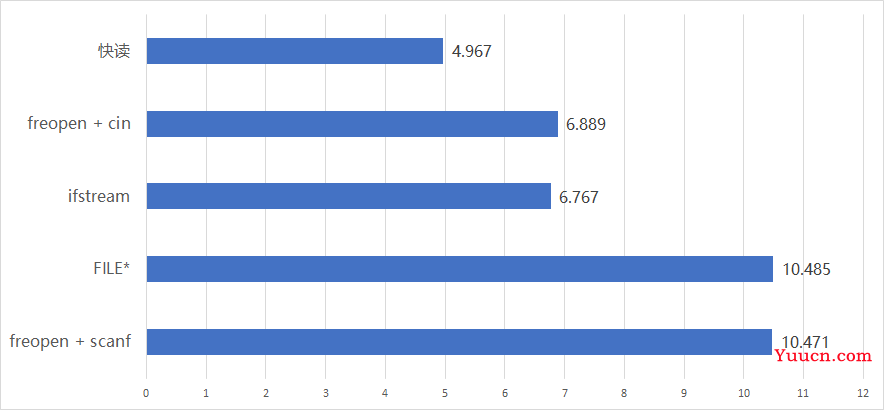
在信息学竞赛中,输入数据规模可能会很大,这时候就需要注意文件读取的效率。本文在 Linux 环境下测试了 C++ 几种常见读入方式的效率。
1. 系统环境
Arch Linux x86_64
默认 Linux 内核,版本 6.1.3
gcc 12.2.0
ext4
2. 测试代码
编译命令(省略文件):g++ -std=c++20,不开优化。
2.0 随机整数(32位有符号)生成
#include <climits>
#include <fstream>
#include <random>
using namespace std;
using i64 = long long;
int main()
{
constexpr int N = 10000;
ofstream fout("in");
random_device rd;
mt19937 gen(rd());
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j)
fout << (i64)gen() + (i64)INT_MIN << ' ';
fout << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
2.1 freopen + scanf
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
freopen("in", "r", stdin);
constexpr int N = 10000;
int x;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j)
scanf("%d", &x);
return 0;
}
2.2 FILE*
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
FILE *fp = fopen("in", "r");
constexpr int N = 10000;
int x;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j)
fscanf(fp, "%d", &x);
return 0;
}
2.3 ifstream
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ifstream fin("in");
constexpr int N = 10000;
int x;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j)
fin >> x;
return 0;
}
2.4 freopen + cin
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
freopen("in", "r", stdin);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
constexpr int N = 10000;
int x;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j)
cin >> x;
return 0;
}
2.5 快读
从洛谷模板题快速排序的最优解复制的快读模板(做了少量修改)
#include <cctype>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
namespace IO
{
class qistream
{
static const size_t SIZE = 1 << 16, BLOCK = 32;
FILE *fp;
char buf[SIZE];
int p;
public:
qistream(FILE *_fp = stdin) : fp(_fp), p(0)
{
fread(buf + p, 1, SIZE - p, fp);
}
void flush()
{
memmove(buf, buf + p, SIZE - p), fread(buf + SIZE - p, 1, p, fp), p = 0;
}
qistream &operator>>(char &str)
{
str = getch();
while (isspace(str))
str = getch();
return *this;
}
template <class T> qistream &operator>>(T &x)
{
x = 0;
p + BLOCK >= SIZE ? flush() : void();
bool flag = false;
for (; !isdigit(buf[p]); ++p)
flag = buf[p] == '-';
for (; isdigit(buf[p]); ++p)
x = x * 10 + buf[p] - '0';
x = flag ? -x : x;
return *this;
}
char getch() { return buf[p++]; }
qistream &operator>>(char *str)
{
char ch = getch();
while (ch <= ' ')
ch = getch();
for (int i = 0; ch > ' '; ++i, ch = getch())
str[i] = ch;
return *this;
}
};
} // namespace IO
int main()
{
FILE *fp = fopen("in", "r");
IO::qistream fin(fp);
constexpr int N = 10000;
int x;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j)
fin >> x;
return 0;
}
3. 测试方法
- 运行一遍随机整数生成。输出的
in文件作为 5 份代码共同的输入文件。 - 依次运行 5 份代码,每份代码运行 5 次,使用 bash 内置
time命令进行计时,取最后 3 次运行时间取平均数。
4. 测试结果
| freopen + scanf | FILE* | ifstream | freopen + cin | 快读 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.471s | 10.485s | 6.767s | 6.889s | 4.967s |